💡 Considered as a major maxim.
Line 11
There’s a better wording for this qaidah, which is the first hadith of 40th hadith of Imam An-Nawawi
Definition
Ruling pertaining to speech and actions are based upon its intentions.
- Example 1 : somebody gives advice, that speech is based on the intention in the heart. Are they sincere? Or do they just want to be praised?
- Example 2 : somebody gives money, when giving money, it could be giving zakat or sadaqah, but it could also be giving a bribe. Therefore, the distinction is in the niat.
- Example 3 : Somebody prays 2 rakaat, from the outside, it’s just praying, it looks the same, but what distinct it is the niat that makes it diferent (are they praying a fard or sunnah prayer)
Evidences
Taken from the Qur’an and Sunnah implicitly.
This is an issue that is very big. Some scholars said it even encompasses a huge portions of Fiqh.
Masail
Benefits (Faidah)
Is looked at 2 different angels
Scolars of Fiqh (Fuqaha)
The importance is when 2 actions are similar on the outside, the intention is what separates them.
- To distinguish an action of worship from an action of habit
- Example : 2 people wake up on a very hot day, and washed their limbs. They did it in a similar way of wudhu. The first person did it with an intention of wudhu for makin salah while the other person did it just to cool down & refresh himself.
- Example : 2 people did not eat from fajr till maghrib. The first perso did it with the intention of weight loss while the other person intended it for sunnah fasting.
- Example : 2 people took showers. The first person did ghusl because their parents taught them to do ghusl whenever they take a shower, making them a habitual action while the other person intended it to purify themselves for friday prayers.
- To distinguish an action of worship from another for of worship
- Example : 2 people prayed 2 rakaats during fajr, the first person performed the sunnah prayer while the other only prayed the fard prayer.
- Example : 2 people fast on a Monday, the first person happen to fast during Ramadhan, while the other fast outside of Ramadhan.
- Example : 2 people did ghusl on a Friday, the first person intended it for Jumuah while the other intended for Janabah.
Scholars of Tazkiyyah (Heart Softeners)
-
To distinguish what is intended behind an action
- Example : 2 people did charity, the first person did it for the sake of Allah while the other intended for Riya’
Talks about the conditon case-by-case, for example, when does the intention come, etc.
Ruling
- Some acts requires intentions, while some does not.
What Requires Intentions
All acts of worship (ibadah), without it, the action is incomplete and you won’t get rewarded.
- But some scholars have exceptions. For example, according to the Hanbali madzhab they believe that hajj for a young child (ghairu mumaiyyaz (age of distinction (at-tamyeez))) does not require intention.
- Difference betwee tamyeez & bulugh : the age of tamyeez is when a child can already distinguish/understand between good and bad while bulugh or baligh is the age of puberty.
Examples of exceptions of niat in ibadah from the Shafii Madzhab :
- Washing the body of a janazah does not require intention
- Does not require intention for doing the adzan because it’s a means to call people to prayer.
Unclear or ambiguous statements.
- Example : when a husband says the following line to his wife “Go back to your family” the wife might think he is divorcing her. However, the husband here does not say it clearly ‘talaq’. In this case we have to look at the person’s intention. What the husband intended is applied.
- Example : When a person says ‘I give my house to charity’. In Islam we know different types of charity. We have to clarify what is the person intention with it, if the person intented for the house to be wakaf, then no one is able to inherit it till yaumul qiyamah.
What Does Not Requires Intentions
At Turuk (Leaving off things)
Examples :
- Leaving off a sin (ribaa, zina, cheating, stealing, etc.)
- Removing of najs
- Repaying of debt
Clear-cut statements
In our sharia there are statements that is clear and can have no other meaning. It does not matter if the person is joking or not, generally, when it is clear, it applies.
- Example : when a man says “I divorce you” to his wife.
Timing
Generally speaking, the beginning of the act of worship (right when you’re about start)
Examples :
✅ Intending to pray salatul fajr right before the takbeer
❌ Have already begun and is in the middle of salatul fajr and realizing not having done the voluntary qabla prayer, then switching the niat in the middle.
✅ A person leaving their home with the intention to pray salatul maghrib in the masjid with the congregation. Once he reached the masjid and is already in the prayer, he only then realized he has not made an intention that a person usually makes just right before the prayer. This is acceptable because the only reason he left in the first place was to pray.
✅ The intention of fasting in Ramadhan is always done prior to the action (the night before).
Nullifiers
- Cutting the intention with another intention.
- Hesitation in the intention.
- Prior intention with firm resolve to break an act of worship.
Examples :
- A traveller who is in the middle of prayer in the masjid, in the 2nd rakaah he intended to break his salah and continue with his journey, and pray later. He intended to break the intention. As he was about to leave, he felt shy. He then continues with the salah. The salah is nullified.
- A person who is praying dzuhur, then in the middle of the prayer they forgot whether they are praying dzuhur or asr. They genuinely have no clue. The salah is nullified.
- A person who intended that they will leave the salah on the 3rd rakaat even before praying. It does not matter if later they change their mind, the salah is nullified.
- A person who felt sick and then they have firm intetion to break their fast. As they walk towards the fridge, they felt like they can continue. They will have to carry on with the current fast while also needing to make up for it.
Place
It’s in the heart. It’s a very easy and simple matter. Do not overthink it. No need to say it out loud.
Qawaid Mundarijat (Sub Principles)
-
Consideration in contracts with intentions and meaning (not by wording or structure)

Example : Person A buys a phone from Person B. Then person B says “I have gifted you my phone for $1000.” Then Person A takes the phone thinking it was gifted to him. However, what Person B intended by the word was a transaction. Therefore it was a transaction, it does not consider the wording.
-
Intentions can specify something general or generalizes something specifc
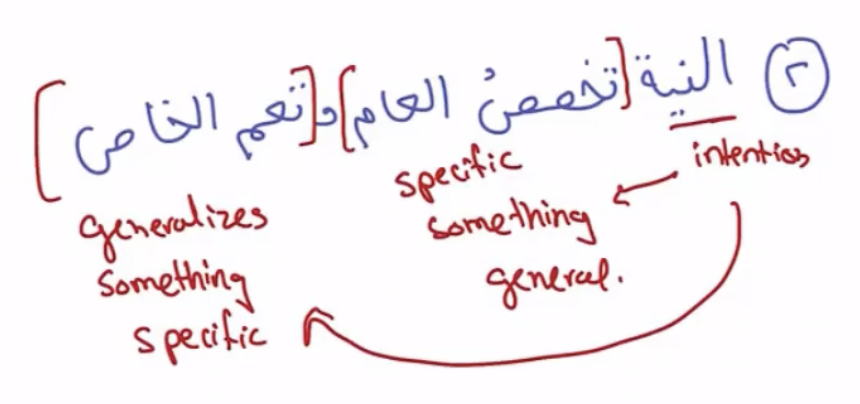
Example : There is a husband and a wife. The husband has a friend over and does not want his wife to be seen. Therefore he said “If I see you enter this room then you are divorced”. The husband’s friend then went to the bathroom, so the wife came into the room. Does this mean that the wife is divorced? It goes back to the intention. If the husband’s intention was more along the line of “If I see you enter this room (whilst my friends are around) then you are divorced” then khalas, no problem. In this case, the intention specifies the general statement he uttered. However, if we take a look from a different angle, the statement “If I see you” is specific. What happens if the wife came in quickly without the husband nor the friend realizing it, does it mean she is not divorced? Back again it goes back to the intention. If the husband’s intention was same with the intention above, meaning, does not matter whether he sees her or not, but she came in whilst his friend was around, then she is divorced.